基本身份驗證
本節詳細介紹了 Spring Security 如何為基於 Servlet 的應用程式提供 HTTP 基本身份驗證支援。
本節描述了 HTTP 基本身份驗證在 Spring Security 中的工作原理。首先,我們看到 WWW-Authenticate 標頭被髮送回未經身份驗證的客戶端
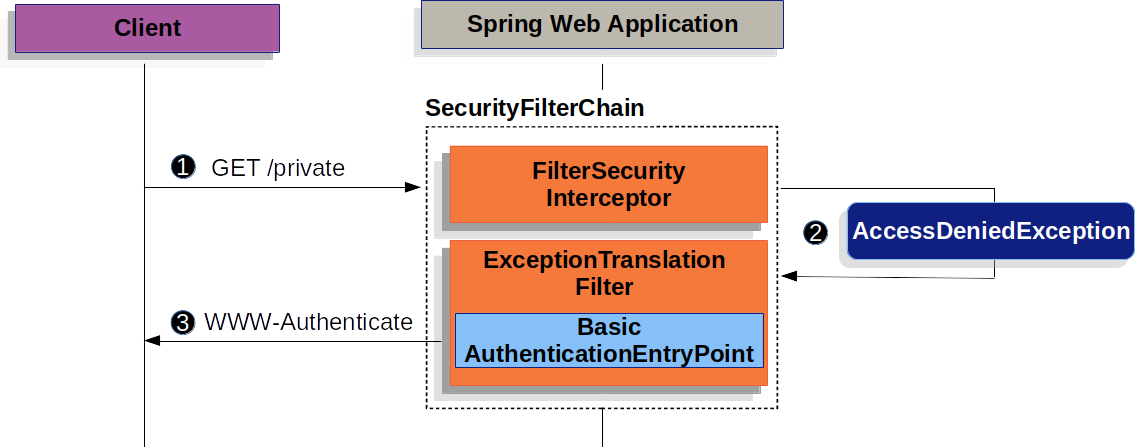
上圖基於我們的 SecurityFilterChain 圖。
![]() 首先,使用者對資源
首先,使用者對資源 /private 發出未經身份驗證的請求,但該請求未經授權。
![]() Spring Security 的
Spring Security 的 AuthorizationFilter 透過丟擲 AccessDeniedException 來表示未經身份驗證的請求被“拒絕”。
![]() 由於使用者未透過身份驗證,
由於使用者未透過身份驗證,ExceptionTranslationFilter 啟動“開始身份驗證”。配置的 AuthenticationEntryPoint 是 BasicAuthenticationEntryPoint 的一個例項,它傳送一個 WWW-Authenticate 標頭。RequestCache 通常是一個 NullRequestCache,它不儲存請求,因為客戶端能夠重播它最初請求的請求。
|
當請求帶有 |
當客戶端收到 WWW-Authenticate 標頭時,它知道應該使用使用者名稱和密碼重試。下圖顯示了處理使用者名稱和密碼的流程
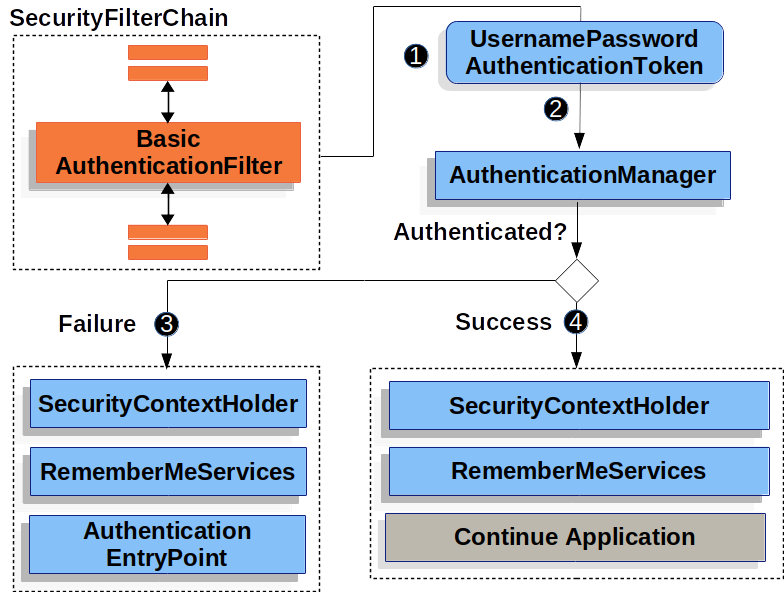
上圖基於我們的 SecurityFilterChain 圖。
![]() 當用戶提交使用者名稱和密碼時,
當用戶提交使用者名稱和密碼時,BasicAuthenticationFilter 透過從 HttpServletRequest 中提取使用者名稱和密碼來建立一個 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken,它是一種 Authentication 型別。
![]() 接下來,
接下來,UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 被傳遞到 AuthenticationManager 進行身份驗證。AuthenticationManager 的具體形式取決於 使用者資訊的儲存方式。
![]() 如果身份驗證失敗,則為“失敗”。
如果身份驗證失敗,則為“失敗”。
-
呼叫
RememberMeServices.loginFail。如果未配置記住我功能,則此操作為空操作。請參閱 Javadoc 中的RememberMeServices介面。 -
呼叫
AuthenticationEntryPoint以再次觸發 WWW-Authenticate 的傳送。請參閱 Javadoc 中的AuthenticationEntryPoint介面。
![]() 如果身份驗證成功,則為“成功”。
如果身份驗證成功,則為“成功”。
-
SecurityContextHolder中任何已透過身份驗證的Authentication都將被載入,並且其許可權將新增到返回的Authentication中。-
呼叫
RememberMeServices.loginSuccess。如果未配置記住我功能,則此操作為空操作。請參閱 Javadoc 中的RememberMeServices介面。 -
BasicAuthenticationFilter呼叫FilterChain.doFilter(request,response)以繼續執行應用程式的其餘邏輯。請參閱 Javadoc 中的BasicAuthenticationFilter類。
預設情況下,Spring Security 的 HTTP 基本身份驗證支援是啟用的。但是,一旦提供了任何基於 Servlet 的配置,HTTP 基本身份驗證必須明確提供。
以下示例顯示了一個最小的、明確的配置
-
Java
-
XML
-
Kotlin
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) {
http
// ...
.httpBasic(withDefaults());
return http.build();
}<http>
<!-- ... -->
<http-basic />
</http>@Bean
open fun filterChain(http: HttpSecurity): SecurityFilterChain {
http {
// ...
httpBasic { }
}
return http.build()
}
