Servlet 認證架構
本討論在 Servlet 安全:全域性概覽 的基礎上,描述了 Spring Security 在 Servlet 認證中使用的主要架構元件。如果您需要具體的流程來解釋這些元件如何協同工作,請參閱 認證機制 特定章節。
-
SecurityContextHolder -
SecurityContextHolder是 Spring Security 儲存 已認證 使用者詳細資訊的地方。 -
SecurityContext - 從
SecurityContextHolder獲取,包含當前已認證使用者的Authentication。 -
Authentication - 可以作為
AuthenticationManager的輸入,提供使用者提供的憑據進行認證;也可以是SecurityContext中當前使用者。 -
GrantedAuthority - 授予
Authentication中主體(即角色、範圍等)的許可權。 -
AuthenticationManager - 定義 Spring Security 過濾器如何執行 認證 的 API。
-
ProviderManager -
AuthenticationManager最常見的實現。 -
AuthenticationProvider - 由
ProviderManager使用,執行特定型別的認證。 -
使用
AuthenticationEntryPoint請求憑據 - 用於向客戶端請求憑據(例如,重定向到登入頁面,傳送WWW-Authenticate響應等)。 -
AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter - 用於認證的基礎
Filter。這也很好地展示了認證的高階流程以及各個元件如何協同工作。
SecurityContextHolder
Spring Security 認證模型的核心是 SecurityContextHolder。它包含 SecurityContext。

SecurityContextHolder 是 Spring Security 儲存 已認證 使用者詳細資訊的地方。Spring Security 不關心 SecurityContextHolder 是如何填充的。如果它包含一個值,則將其用作當前已認證的使用者。
指示使用者已認證的最簡單方法是直接設定 SecurityContextHolder
SecurityContextHolder-
Java
-
Kotlin
SecurityContext context = SecurityContextHolder.createEmptyContext(); (1)
Authentication authentication =
new TestingAuthenticationToken("username", "password", "ROLE_USER"); (2)
context.setAuthentication(authentication);
SecurityContextHolder.setContext(context); (3)val context: SecurityContext = SecurityContextHolder.createEmptyContext() (1)
val authentication: Authentication = TestingAuthenticationToken("username", "password", "ROLE_USER") (2)
context.authentication = authentication
SecurityContextHolder.setContext(context) (3)| 1 | 我們首先建立一個空的 SecurityContext。您應該建立一個新的 SecurityContext 例項,而不是使用 SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authentication),以避免在多個執行緒之間發生競爭條件。 |
| 2 | 接下來,我們建立一個新的 Authentication 物件。Spring Security 不關心 SecurityContext 上設定的 Authentication 實現型別。這裡,我們使用 TestingAuthenticationToken,因為它非常簡單。更常見的生產場景是 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(userDetails, password, authorities)。 |
| 3 | 最後,我們將 SecurityContext 設定在 SecurityContextHolder 上。Spring Security 使用此資訊進行 授權。 |
要獲取有關已認證主體的資訊,請訪問 SecurityContextHolder。
-
Java
-
Kotlin
SecurityContext context = SecurityContextHolder.getContext();
Authentication authentication = context.getAuthentication();
String username = authentication.getName();
Object principal = authentication.getPrincipal();
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities = authentication.getAuthorities();val context = SecurityContextHolder.getContext()
val authentication = context.authentication
val username = authentication.name
val principal = authentication.principal
val authorities = authentication.authorities預設情況下,SecurityContextHolder 使用 ThreadLocal 來儲存這些詳細資訊,這意味著 SecurityContext 始終可用於同一執行緒中的方法,即使 SecurityContext 未作為引數顯式傳遞給這些方法。以這種方式使用 ThreadLocal 是非常安全的,只要您在處理完當前主體的請求後注意清除執行緒即可。Spring Security 的 FilterChainProxy 確保 SecurityContext 始終被清除。
有些應用程式並不完全適合使用 ThreadLocal,因為它們處理執行緒的方式特殊。例如,Swing 客戶端可能希望 Java 虛擬機器中的所有執行緒都使用相同的安全上下文。您可以在啟動時為 SecurityContextHolder 配置策略,以指定您希望如何儲存上下文。對於獨立應用程式,您將使用 SecurityContextHolder.MODE_GLOBAL 策略。其他應用程式可能希望由安全執行緒派生的執行緒也假定相同的安全身份。您可以透過使用 SecurityContextHolder.MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL 來實現此目的。您可以透過兩種方式更改預設的 SecurityContextHolder.MODE_THREADLOCAL 模式。第一種是設定系統屬性。第二種是呼叫 SecurityContextHolder 上的靜態方法。大多數應用程式不需要更改預設設定。但是,如果您需要更改,請檢視 SecurityContextHolder 的 JavaDoc 以瞭解更多資訊。
SecurityContext
SecurityContext 從 SecurityContextHolder 獲取。SecurityContext 包含一個 Authentication 物件。
Authentication
Authentication 介面在 Spring Security 中主要有兩個用途
-
作為
AuthenticationManager的輸入,提供使用者提供的憑據以進行認證。在這種情況下,isAuthenticated()返回false。 -
表示當前已認證使用者。您可以從 SecurityContext 獲取當前的
Authentication。
Authentication 包含
-
principal:標識使用者。使用使用者名稱/密碼進行認證時,這通常是UserDetails的例項。 -
credentials:通常是密碼。在許多情況下,使用者認證後會清除此項,以確保其不會洩露。 -
authorities:GrantedAuthority例項是授予使用者的高階許可權。兩個示例是角色和範圍。
它還配備了一個 AdditionalRequiredFactorsBuilder,允許您修改現有的 Authentication 例項並可能將其與另一個合併。這在需要從一個認證步驟(如表單登入)獲取許可權並將其應用於另一個認證步驟(如一次性令牌登入)的場景中非常有用,如下所示
-
Java
-
Kotlin
Authentication lastestResult = authenticationManager.authenticate(authenticationRequest);
Authentication previousResult = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
if (previousResult != null && previousResult.isAuthenticated()) {
lastestResult = lastestResult.toBuilder()
.authorities((a) -> a.addAll(previous.getAuthorities()))
.build();
}var latestResult: Authentication = authenticationManager.authenticate(authenticationRequest)
val previousResult = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().authentication;
if (previousResult?.isAuthenticated == true) {
latestResult = latestResult.toBuilder().authorities { a ->
a.addAll(previousResult.authorities)
}.build()
}GrantedAuthority
GrantedAuthority 例項是授予使用者的高階許可權。兩個示例是角色和範圍。
您可以從 Authentication.getAuthorities() 方法獲取 GrantedAuthority 例項。此方法提供一個 GrantedAuthority 物件的 Collection。GrantedAuthority 顧名思義,是授予主體的許可權。此類許可權通常是“角色”,例如 ROLE_ADMINISTRATOR 或 ROLE_HR_SUPERVISOR。這些角色隨後用於 Web 授權、方法授權和領域物件授權。Spring Security 的其他部分會解釋這些許可權並期望它們存在。在使用基於使用者名稱/密碼的認證時,GrantedAuthority 例項通常由 UserDetailsService 載入。
通常,GrantedAuthority 物件是應用程式範圍的許可權。它們不特定於給定的領域物件。因此,您不太可能擁有一個 GrantedAuthority 來表示對 Employee 物件編號 54 的許可權,因為如果有數千個這樣的許可權,您很快就會耗盡記憶體(或者,至少會導致應用程式認證使用者花費很長時間)。當然,Spring Security 明確設計用於處理這種常見需求,但您應該為此目的使用專案的領域物件安全功能。
AuthenticationManager
AuthenticationManager 是定義 Spring Security 過濾器如何執行 認證 的 API。返回的 Authentication 隨後由呼叫 AuthenticationManager 的控制器(即 Spring Security 的 Filters 例項)設定到 SecurityContextHolder 上。如果您沒有與 Spring Security 的 Filters 例項整合,您可以直接設定 SecurityContextHolder,並且不需要使用 AuthenticationManager。
雖然 AuthenticationManager 的實現可以是任何型別,但最常見的實現是 ProviderManager。
ProviderManager
ProviderManager 是 AuthenticationManager 最常用的實現。ProviderManager 將認證委託給一個 AuthenticationProvider 例項的 List。每個 AuthenticationProvider 都有機會指示認證應該成功、失敗,或者指示它無法做出決定並允許下游的 AuthenticationProvider 做出決定。如果沒有一個配置的 AuthenticationProvider 例項能夠進行認證,則認證失敗,並丟擲 ProviderNotFoundException,這是一個特殊的 AuthenticationException,表示 ProviderManager 未配置為支援傳遞給它的 Authentication 型別。
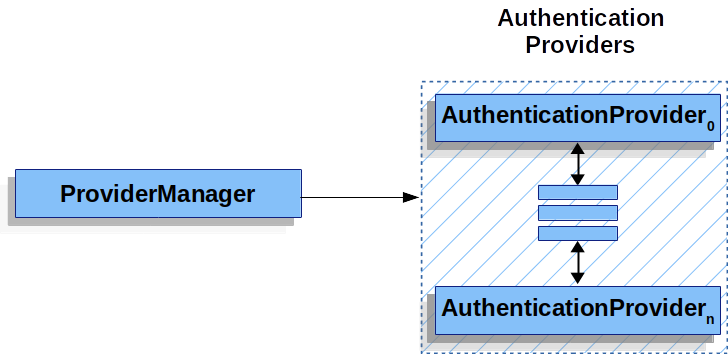
實際上,每個 AuthenticationProvider 都知道如何執行特定型別的認證。例如,一個 AuthenticationProvider 可能能夠驗證使用者名稱/密碼,而另一個可能能夠認證 SAML 斷言。這使得每個 AuthenticationProvider 都能執行非常特定型別的認證,同時支援多種認證型別並僅暴露一個 AuthenticationManager bean。
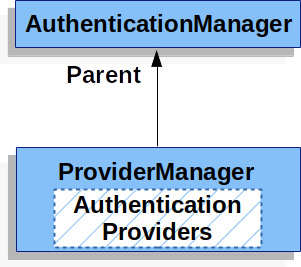
ProviderManager 還允許配置一個可選的父級 AuthenticationManager,當沒有任何 AuthenticationProvider 能夠執行認證時,將諮詢該父級。父級可以是任何型別的 AuthenticationManager,但它通常是 ProviderManager 的一個例項。
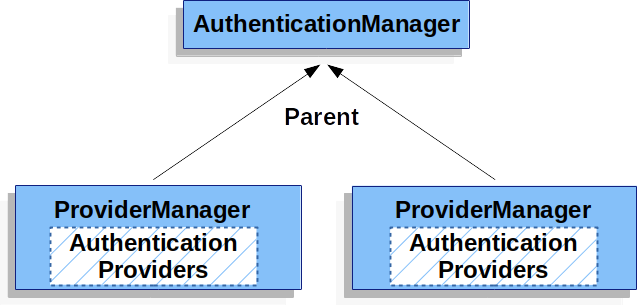
事實上,多個 ProviderManager 例項可能共享同一個父 AuthenticationManager。這在存在多個 SecurityFilterChain 例項,它們具有一些共同的認證(共享的父 AuthenticationManager),但也有不同的認證機制(不同的 ProviderManager 例項)的場景中相當常見。
預設情況下,ProviderManager 會嘗試清除成功認證請求返回的 Authentication 物件中的任何敏感憑據資訊。這可以防止密碼等資訊在 HttpSession 中保留的時間超過必要。
|
|
當您使用使用者物件快取時(例如,為了提高無狀態應用程式的效能),這可能會導致問題。如果 Authentication 包含對快取中物件的引用(例如 UserDetails 例項)並且其憑據被移除,則不再可能根據快取的值進行認證。如果您使用快取,則需要考慮這一點。一個顯而易見的解決方案是首先複製物件,無論是在快取實現中還是在建立返回的 Authentication 物件的 AuthenticationProvider 中。或者,您可以停用 ProviderManager 上的 eraseCredentialsAfterAuthentication 屬性。請參閱 ProviderManager 類的 Javadoc。
AuthenticationProvider
您可以將多個 AuthenticationProvider 例項注入 ProviderManager。每個 AuthenticationProvider 執行特定型別的認證。例如,DaoAuthenticationProvider 支援基於使用者名稱/密碼的認證,而 JwtAuthenticationProvider 支援認證 JWT 令牌。
使用 AuthenticationEntryPoint 請求憑據
AuthenticationEntryPoint 用於傳送 HTTP 響應,從客戶端請求憑據。
有時,客戶端會主動包含憑據(例如使用者名稱和密碼)來請求資源。在這種情況下,Spring Security 無需提供從客戶端請求憑據的 HTTP 響應,因為它們已經包含在內。
在其他情況下,客戶端對未經授權訪問的資源發出未經認證的請求。在這種情況下,將使用 AuthenticationEntryPoint 的實現來向客戶端請求憑據。AuthenticationEntryPoint 實現可能會執行 重定向到登入頁面,響應 WWW-Authenticate 標頭,或採取其他操作。
AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter
AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter 用作認證使用者憑據的基礎 Filter。在憑據可以被認證之前,Spring Security 通常會使用 AuthenticationEntryPoint 來請求憑據。
接下來,AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter 可以認證提交給它的任何認證請求。
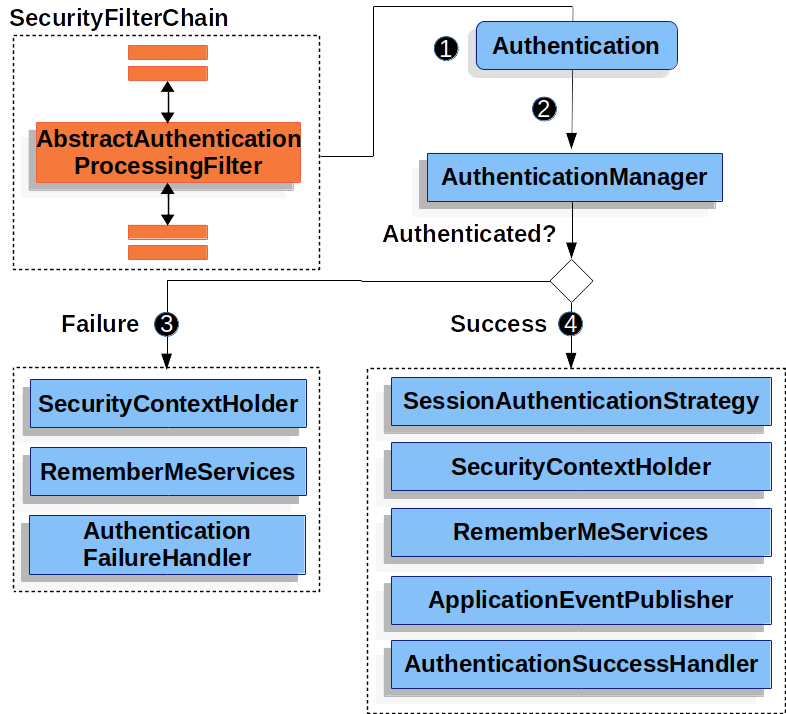
![]() 當用戶提交憑據時,
當用戶提交憑據時,AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter 從 HttpServletRequest 建立一個 Authentication 以進行認證。建立的 Authentication 型別取決於 AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter 的子類。例如,UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 從 HttpServletRequest 中提交的 *使用者名稱* 和 *密碼* 建立一個 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken。
![]() 接下來,將
接下來,將 Authentication 傳遞給 AuthenticationManager 進行認證。
![]() 如果認證失敗,則為 *失敗*。
如果認證失敗,則為 *失敗*。
-
呼叫
RememberMeServices.loginFail。如果未配置記住我功能,則此操作為空操作。請參閱 rememberme 包。 -
呼叫
AuthenticationFailureHandler。請參閱AuthenticationFailureHandler介面。
![]() 如果認證成功,則為 *成功*。
如果認證成功,則為 *成功*。
-
SessionAuthenticationStrategy會收到新登入的通知。請參閱SessionAuthenticationStrategy介面。 -
載入 SecurityContextHolder 中任何已認證的
Authentication,並將其許可權新增到返回的 Authentication 中。 -
將 Authentication 設定到 SecurityContextHolder 上。稍後,如果您需要儲存
SecurityContext以便其可以自動設定到未來的請求中,則必須顯式呼叫SecurityContextRepository#saveContext。請參閱SecurityContextHolderFilter類。 -
呼叫
RememberMeServices.loginSuccess。如果未配置記住我功能,則此操作為空操作。請參閱 rememberme 包。 -
ApplicationEventPublisher釋出InteractiveAuthenticationSuccessEvent。 -
呼叫
AuthenticationSuccessHandler。請參閱AuthenticationSuccessHandler介面。

